There Is Many Brand And Different Type Of Design Of Telescope. Basic Function Of A Telescope. How To Decide Which Is Best Is To Understand What Telescope Is, What Component It Consist Of And Needed, Difference Between Visual And Imaging Pathway
Telescope Function
- To Gather Light
- To Increase Magnification
- To Increase Resolution
Subdivision Of Telescope Selection
- Manual Telescope
- Phone Assisted Telescope
- Computerized Telescope
- Smart Telescope
- Astrophotography Telescope
Choice Depends On
- Visual - All Telescope Except Smart Telescope, Or Dedicated Astrophotography Depends on Configuration
- Photography - All Telescope Can Do But Some Are Better For Division Of Astrophotography -Planets, Lunar, Solar, Deep Space Objects, Infrared, X-Ray Etc Might Need Different Optical Configuration
- Design Based For Visual Aspect
- Refractor - Portable For Small But Less Portable For Large. Excellent Image Sharpness And Contrast, Suffer From Chromatic Aberration And Field Curvature
- Reflector - Less Portable Due To Size, Ligther When Bigger, Excellent Image Sharpness And Contrast, Lowest Cost For Big Aperature. Usually Suffer From Coma Or Spherical Aberration
- Cassegrain - Portable For Large Size But Heavier When Bigger, Excellent Image Sharpness, But Less Contrast. Usually Suffer From Coma And Field Curvature
- Design Based For Photography Aspect
- Refractor - Portable, Simple To Get Decent Image. For Wide And Medium Angle DSO, Moon As Whole, Solar In Ha, Cal-K, White Light, ND ETC
- Reflector - Less Portable, Excellent Performance For Price, Can Do Both Medium Angle DSO (Higher Resolution Than Refractor), Moon, Lunar Crates, Solar In White Light, ND, Planetary - Jack Of All Trade
- Cassegrain - Medium Portability, Excellent In Planetary, Medium Angle And Small DSO, Lunar Crates, Moon, Solar
- Smart Telescope - Ideal For Medium Angle DSO, Moon, Sun In White Light or ND
Rule Of Telescope Performance And Decision Of Making
- Bigger Optics Have Better Resolution, Magnfication And Brightness, In Visual Or Photography
- Bigger Telescope Will Be Bulkier And Heavier, So Consideration Will Be On Maximum Size And Weight That Is Consider Portable. General Rule If Big Telescope For 1 Person Is Around 8-10'' Aperature Size
Telescope Have 3 Most Important Component
- Optical Tube (Optics)
- Tripod (Supporting Leg)
- Mount (Movement Arm)
Telescope (Head) Primary Function Is :-
- To Magnify Object
- To Amplify Brightness Of Object (Magnitude Of Brightness)
- Increase Resolution Of Object (Angular Seperation)
Tripod (Leg) Function Is :-
- As Support Of Tube And Mount
Mount (Neck) Function Is :-
- Allow Movement Of Optical Tube
Basic Understanding Of Telescope Optics
- Design Of Telescope - Telescope Have 3 Primary Different Design : Refractor, Reflector And Also Cassegrain
- Refractor Are Most Simple Design, Involving Focusing Incoming Light Source To Single Point. Large Objective Lens Gather Light And Focus It To Increase Image Detail And Brightness

Refractor Telescope
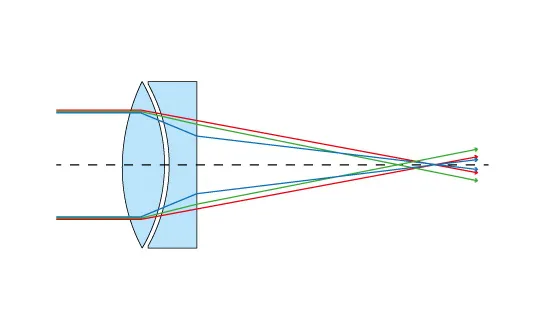
Refractor Provide Highest Contrast View Because Of No Central Obstruction, But Due To Design That Causes Light Refraction, This Will Scatter Light Of Different Colour Spectrum Resulting Chromatic Aberation (Colour Fringing) Best Optical Refractor Design Using Special Low Dispersion (ED) Glasses Will Reduce This Problem But Will Be More Costly
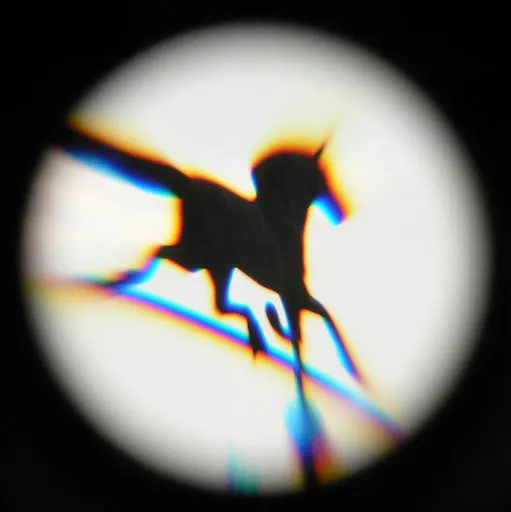

Chromatic Aberation Seen As Blue/Brown/Purple Colour Fringing
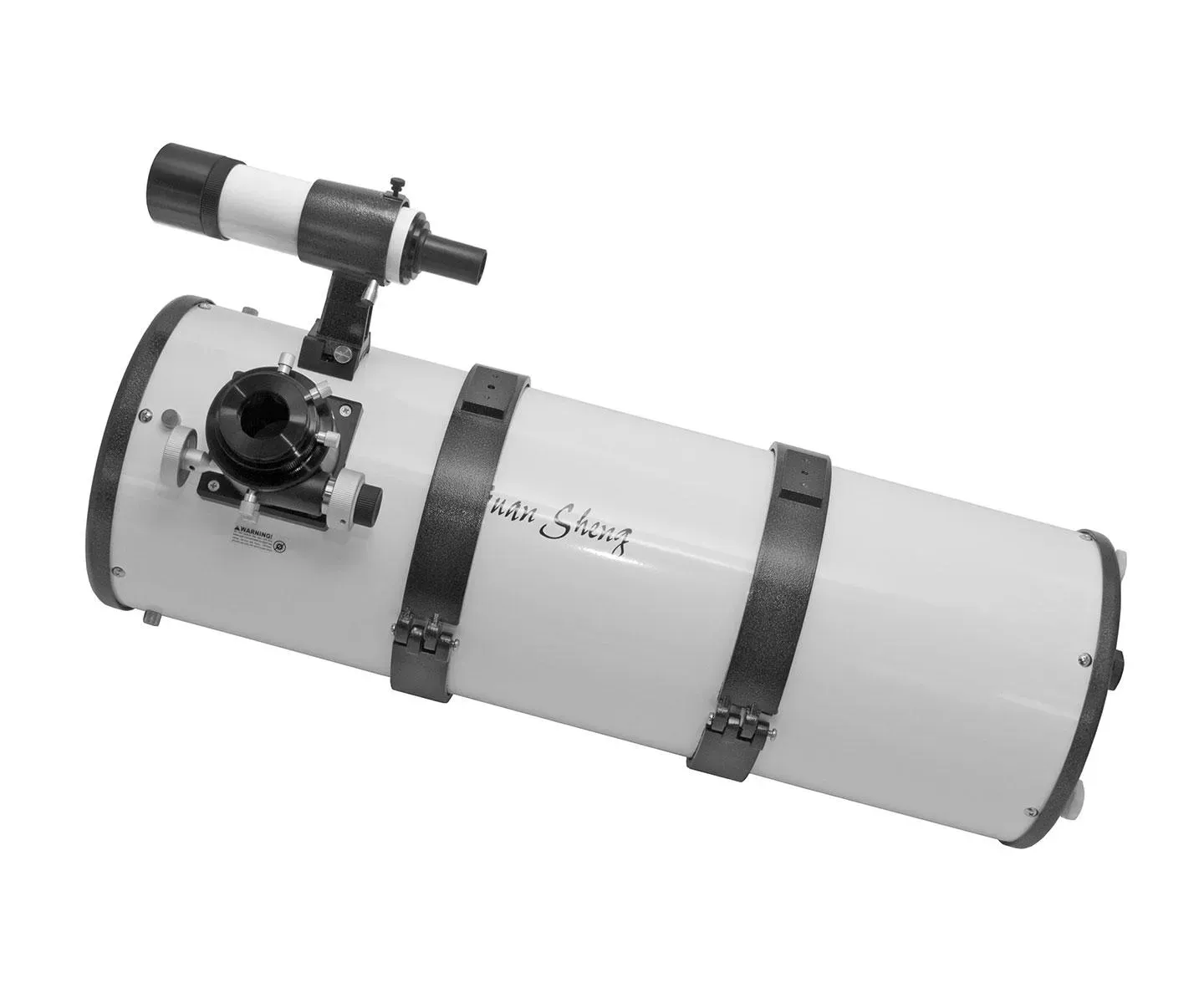

Reflector Telescope
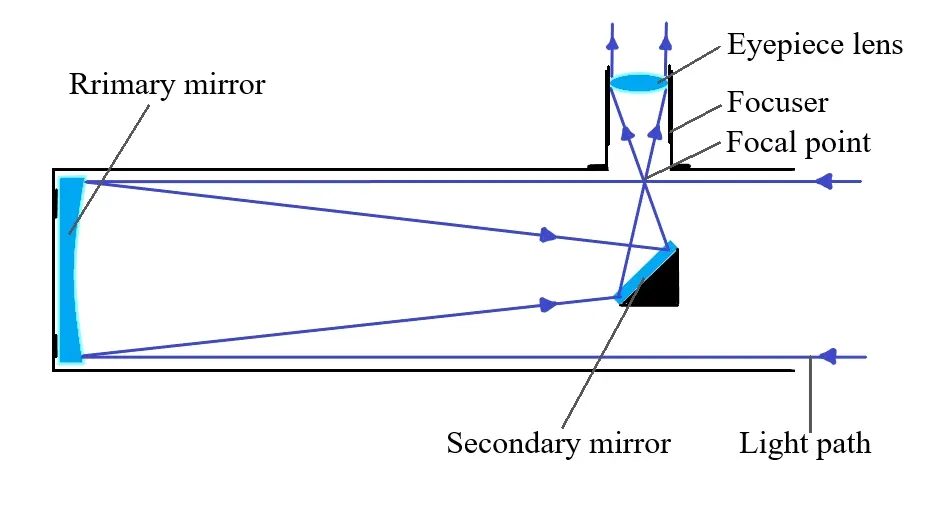
Reflector Basically Are Reflection Mirror. Precision Polish Reflecting Mirror Will Focus Light From Mirror To Increase Image Brightness And Detail. Mirror Are Easier To Manufacture And Cost Less Than Lens (Bigger Aperature For Price). Reflector Does Not Suffer From Chromatic Aberation And Provide Almost Similar Contrast To Refractor. Reflector Can Be Built With Spherical, Hyperbolic Or Parabolic Mirror. Parabolic Mirror Can Give Diffraction Limited Optics But Cost More. Hyperbolic Are Special Design For Astrophotography Purpose. Spherical Mirror Gives Good Image If Focal Ratio Exceed F/10, Anything Under Will Require Spherical Lens Corrector (Known As Jones-Bird Newtonian)
Cassegrain Telescope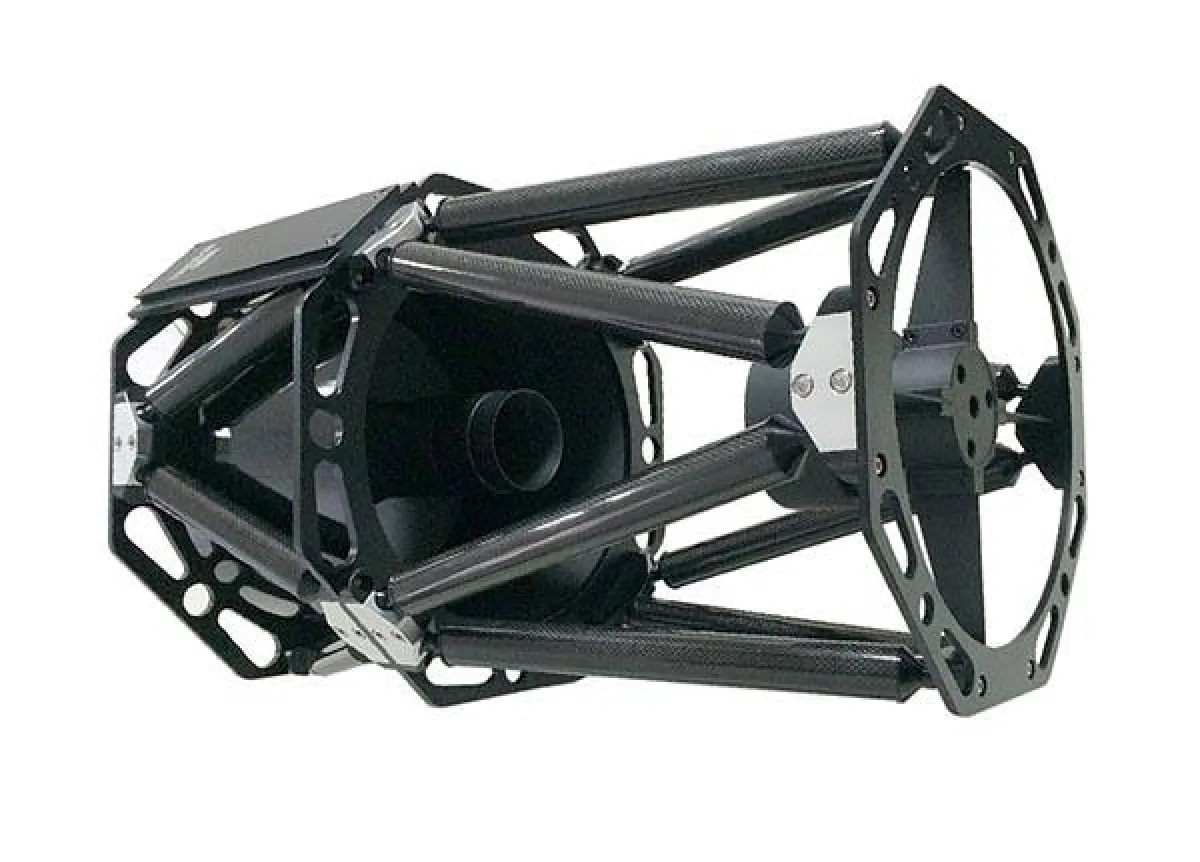
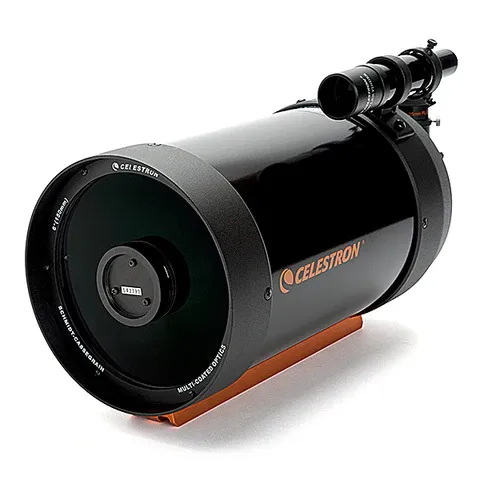
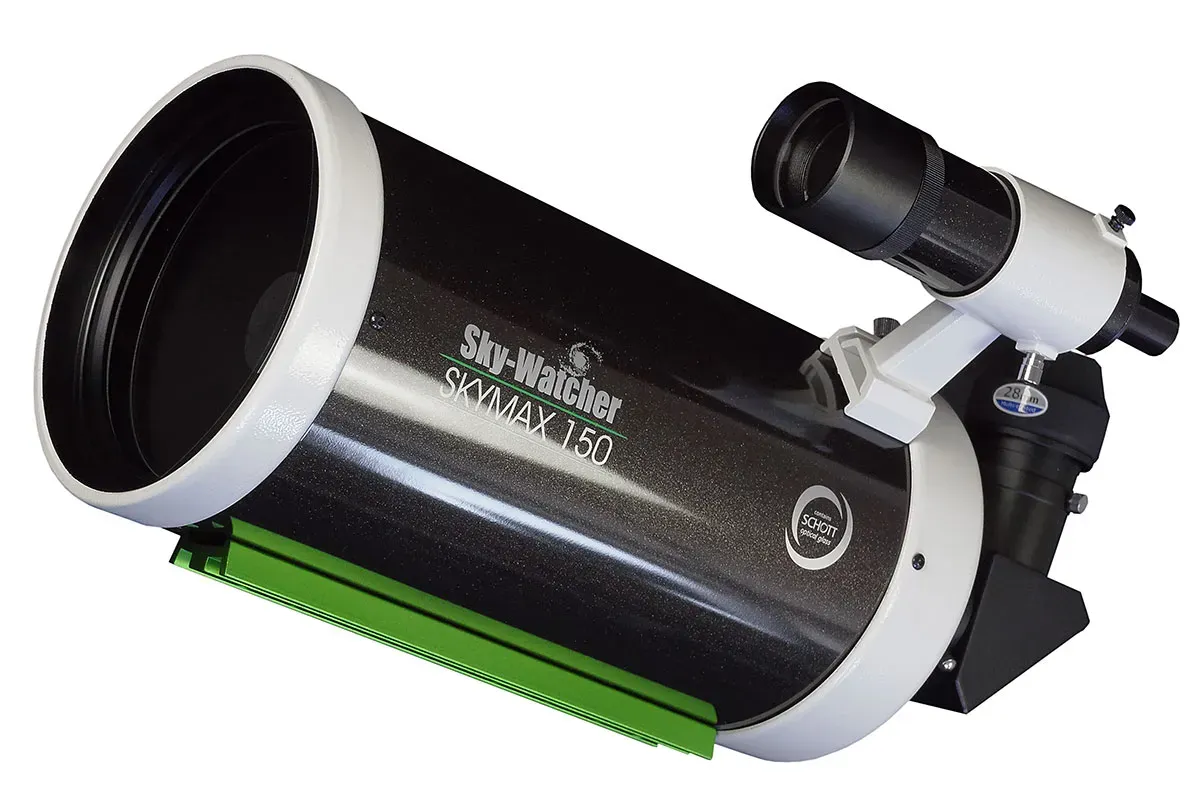


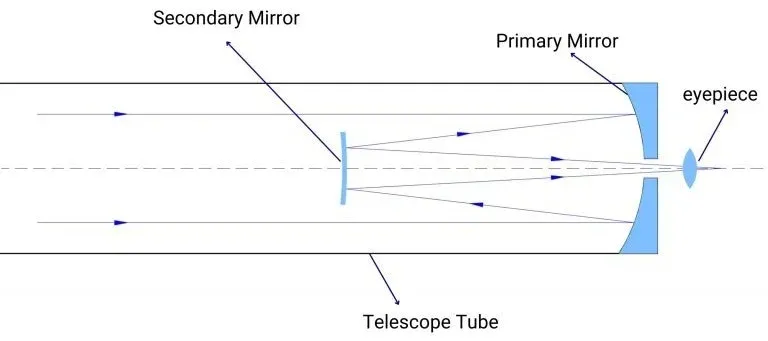
Cassegrain Have 2 Primary Type Of Cassegrain - Catadioptric Cassegrain And Reflector Cassegrain. Both Works Primary Using 2 Reflective Mirror (Which Can Be Spherical, Parabolic. Elliptical Or Hyperbolic). Catadioptric Use Additional Corrector Lens In Front Of Telescope, While Some Design Uses Sub-Aperature Corrector
Catadioptric Are Compound Telescope (Folding Optics). This Design Allow More Compact Telescope For Aperture But Cost More. Common Type Of Cassegrain
- Schmidt Cassegrain (SCT)
- Maksutov Cassegrain (MCT)
- Classical Cassegrain
- Ritchey Chretien
- Dall Kirkham
- Klevtsov Cassegrain
Cassegrain Involve Folding Optical Path Multiple Time To Achieve Compact For Aperature Telescope
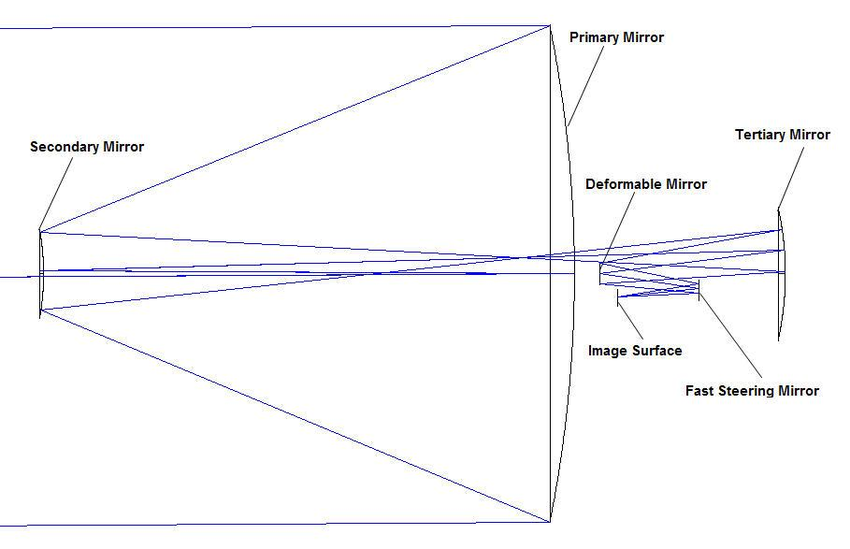
Three Mirror Anastigmat
Advance Design Usually Found In Research Grade Observatory. Design With 3 curved Mirror Eliminate Spherical Aberration, Coma And Astigmatism. It Is Found In Some Of World Largest Telescope Includes James Webb Telescope And Extremely Large Telesocope (ELT)
Designs Includes
- Paul Baker Telescope
- Korsch Telescope
- Eisenberg-Pearson Telescope
- Factor Determining Telescope Optical Performance
- Important Determination Of Telescope Performance Is Aperture (Size Of Objective). Bigger Aperature Allow Higher Light Collection And Image Resolution (Under Best Condition).
- Central Obstruction Determine TContrast And Brightness Of Image
- Light Gathering Power Determined By Aperture Of A Telescope. Higher Light Gathering Power Translate To Brighter Image Of Deep Space Object.
- Resolution Of Telescope Is Determined By Aperture. Resolution Of Telescope Is Measure By Dawes Limit (Typical In Arc Second) A Smaller Dawes Limit Translate To Better Capability Of Telescope To Detect And Differentiate Fine Detail Of Objects
- Optical Coating : Multi-Coated Lens Will Reduce Light Loss From Reflection Of Glass. In Refractor Telescope, Uncoated Glass Gives About 8% Light Loss, Where As Multi-Coated Refractor Loss Less Than 0.5% Of Total Light. In Case Of Reflector, Coating Quality Will Depends On Type Of Aluminium Used And Measured In Reflectivity Index. Best Reflectivity Index Is 99% Reflectivity
- Optical Perfection : Mirror Or Lens Perfection Is Calculated Based On Diffraction Limit. Diffraction Limited Optics Translate To Almost Perfect Mirror, Where Maximum Resolution Is Possible With Usage Of Diffraction Limited Lens/Mirror.
- Optical Aberation : Mirror Or Lens Causes Deviation Of Light Pathway. Common Optical Aberration Includes Spherical Abberation, Coma, Field Curvature, Astigmatism and Spherical aberration
- Recommended Maximum Performance Of Telescope And How It Is Calculated
- Magnification : Maximum Magnification Of Telescope Is Calculated Based On Aperature Of Telescope. General Rule Of 50-60x Per Inch (25.2mm) Of Aperature Is Maximum Magnification Of Given Telescope. 50mm Telescope Will Have 120x Maximum Magnification. 203mm (8'') Telescope Will Have 480x Maximum Magnification
- Light Gathering Power : Light Gathering Power Will Translate To How Bright An Object Seen Via Telescope. Higher Light Gathering Power Allow Dimmer Objects Seen Brighter And With More Detail. Light Gathering Power Is calculated Based On Aperature (Size Of Telescope Lens/Mirror) 70mm Telescope Has 70x70/49 : 100x Light Gathering Power. 203mm (8'') Telescope Has 203x203/49 : 841x Light Gathering Power. Higher Light Gathering Power, Dimmer Deep Space Object Can Be Seen
- Optimizing Magnification Is Based On Light Gathering Power. Telescope With 100x Light Gathering Power Maybe Best To Use At 100x Zoom As Higher Zoom Will Cause Image To Be Dimmer Than What Eye Is Seeing, Which 100x Light Gathering Power Operating At 25x Zoom Will Have 4x Brighter That What Eye Can Be See
Tripod (Leg)
Tripod Is One Of Most Important Component Of Telescope And Commonly Misundestood Component. Tripod Is Not For Movement Of Telescope Tube, But Rather As Support For Tube And Mount. Decision On Tripod Is Based On Factor Of Stability, Height, Weight And Size. Not All Telescope Need Tripod As Some Telescope Like Dobsonian Mount Are Big Enough To Act Like Leg For Telescope Tube
Tripod Construction Material Will Determine Performance Of Telescope
- Solid Wood - Light Weight, Strong, Stable, Big Size But Cost More
- Aluminium - Light Weight, less stable, Medium To Strong (Depends On Thickness), Big Size But Cost More
- Steel - Heavier, Strong, stable, Big Size And Lower Cost
- Carbon Fiber - Ultra Light Weight, Strong, Stability Subjective To Scope Size, Compact But Highest Cost
- Dobsonian - Big, Stable, Strong, Heavy. Not An Actual Tripod But Work Like Tripod With Mount
Mount (Neck)
Mount Is Neck That Connect Telescope And Tripod Allowing Movement. Mount Are Dividend Into 2 Movement System - Alt Azimuth And Equatorial
Alt Azimuth Mount
- Simple Up Down Left Right Movement
- Excellent For Visual And Planetary Photography
- Can Be Use For Deep Space Photography With Shorter Exposure Or Field Derotator
Equatorial
- Give Accurate Coordinate Of Objects
- Excellent For Photography Of Deeps Space Objects As Well As Planets
- Can Be Use For Visual But Longer Time To Setup